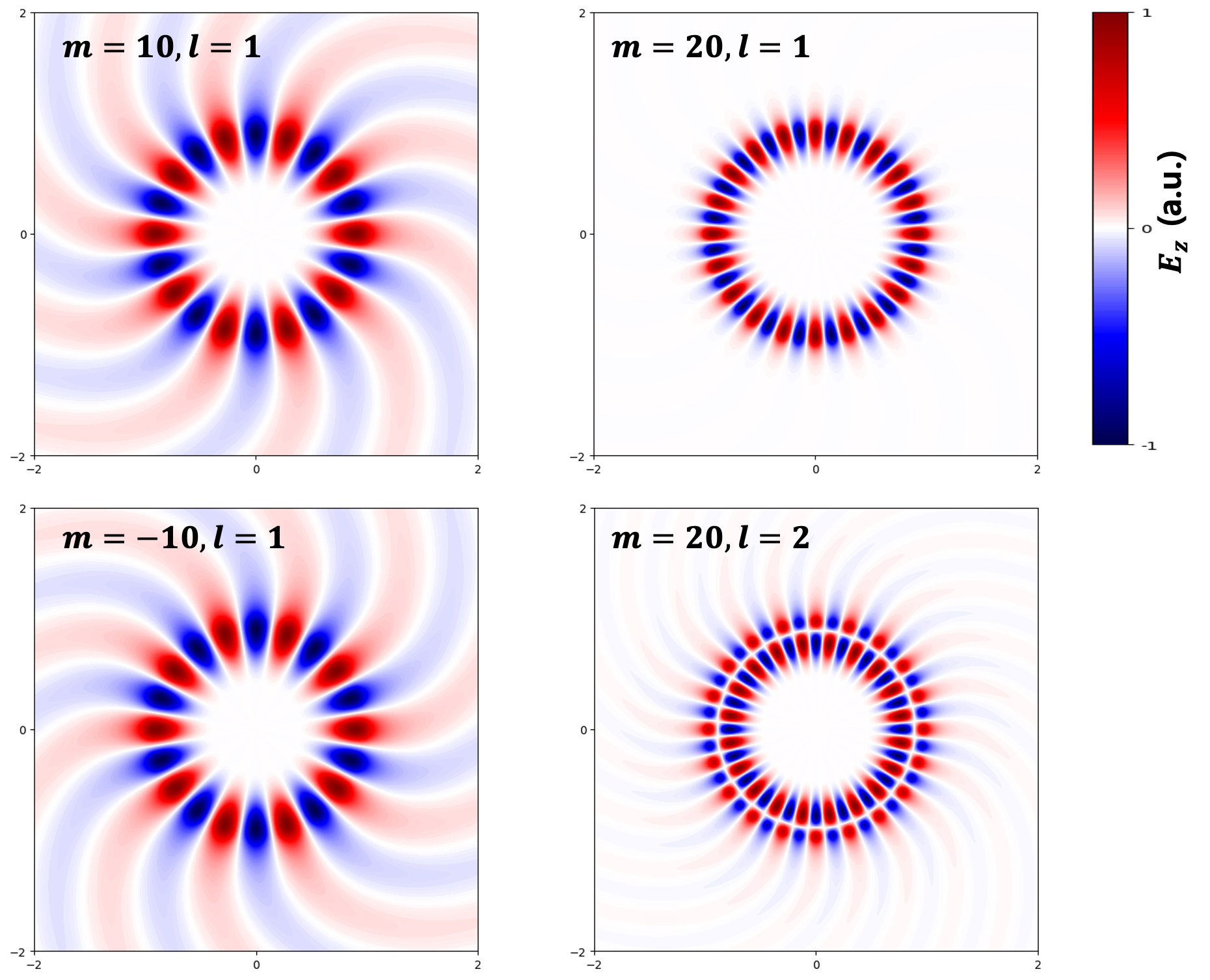
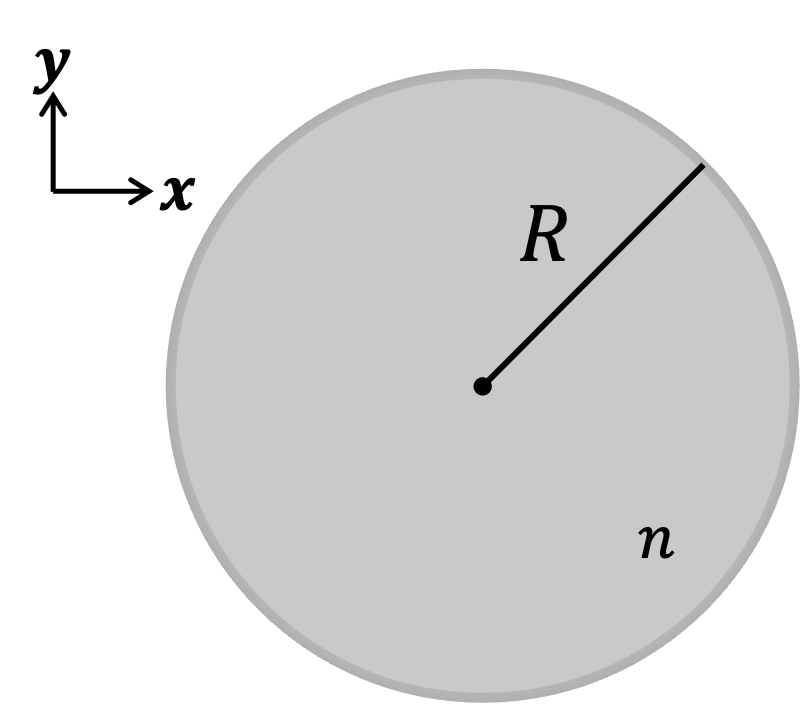
circular disk cavity
Whispering Gallery Modes
From equation (7) of [Modes of Slab Waveguide] the scalar mode equation can be expressed by
Since the system has rotational symmetry, the ansatz $\psi(r,\phi) = \Psi(r)e^{im\phi}$ is used. where the $2\pi$ periodicity implies $m \in \mathbb{Z}$ and can be connected with the slab waveguide propagtion constant as $\beta=\frac{m}{R}$. Then by assuming $k_z \approx 0$ that propagation in the z-direction is negligible,
is obtained. which is Bessel-like ODE that can be solved independently by Bessel, Hankel an Neumann functions.
With outgoing wave condition, the reasonable ansats is
where the refractive index outside the cavity is assumed zero. Now applying the boudary condition for electromagnetic waves yields,
where $x=kR, \zeta=1(n^2)$ for TM(TE) pol.
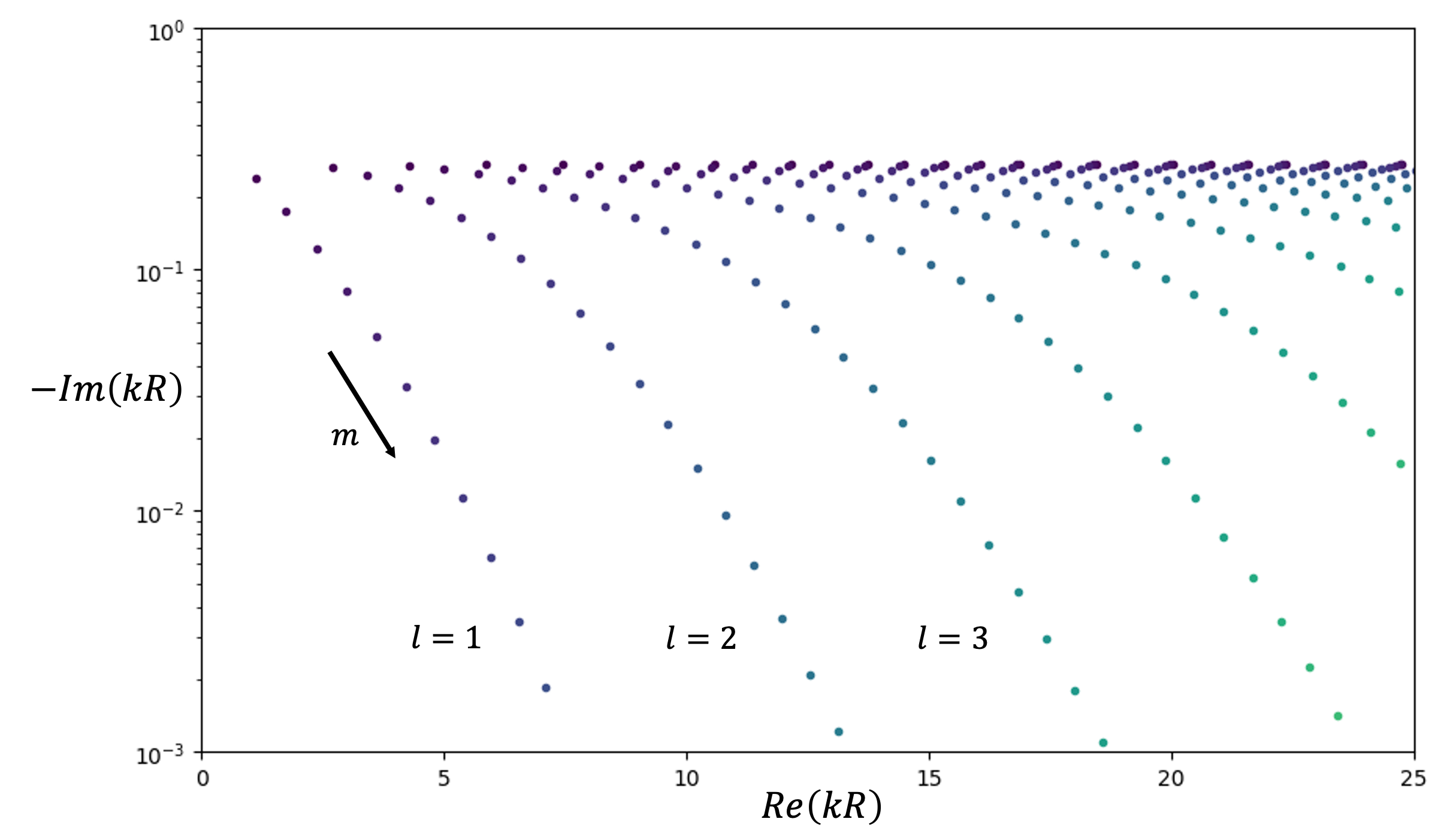
$kR$ values are complex with $\Re(kR)=\frac{2\pi R}{\lambda}, Q=\frac{\Re(kR)}{-2\Im(kR)}$